01
Zero Trust and Ransomware
The current state of ransomware attacks
What is Zero Trust
⏱ Avg. Reading Time: 5 min
The current state of ransomware attacks
What is Zero Trust
How Zero Trust mitigates ransomware attacks
Securing the organization with zero trust
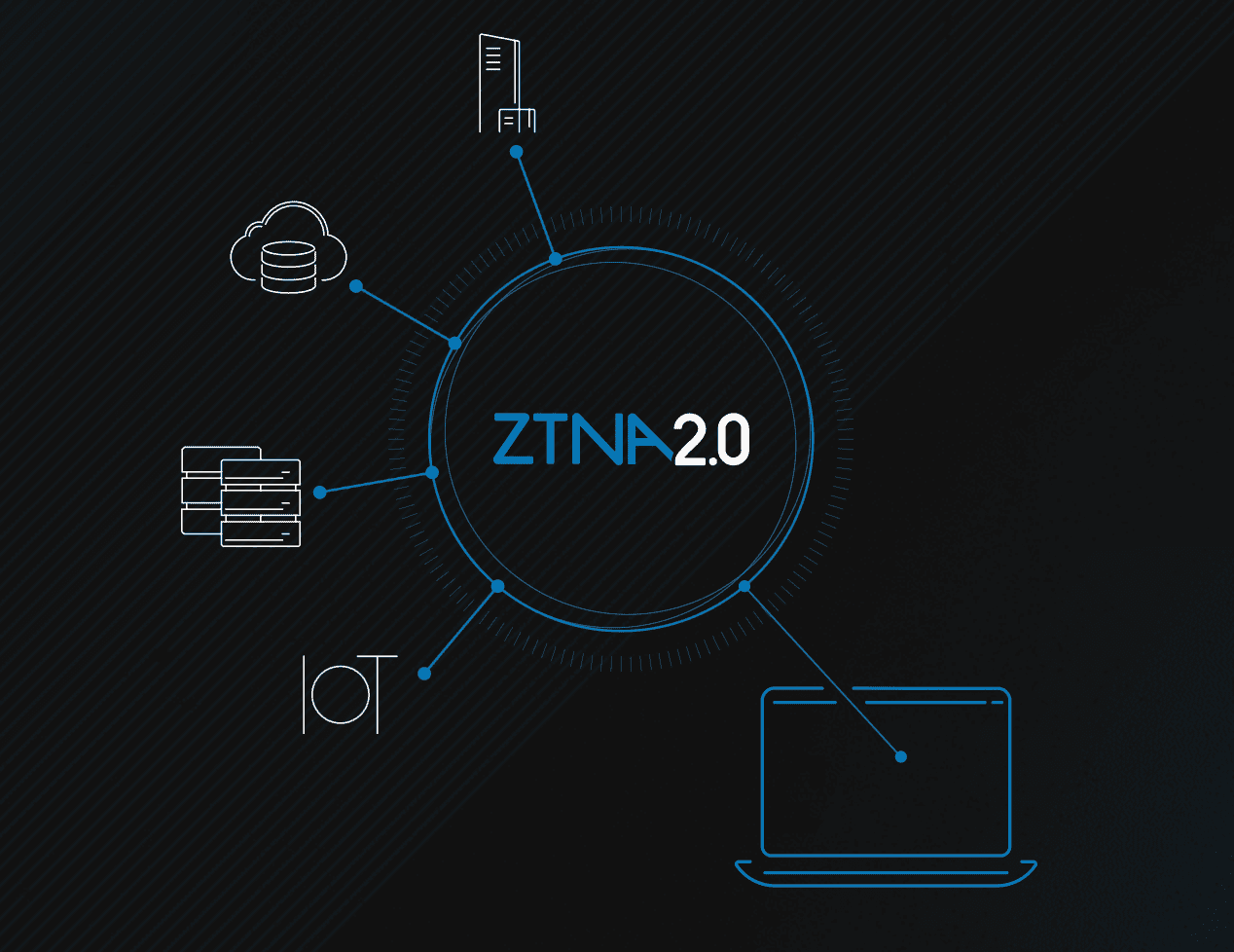
ZTNA vs. VPNs
Choosing a ZTNA provider
A phased approach to Zero Trust adoption
Ransomware attackers are blocked from accessing critical applications.
Ransomware attackers are prevented from moving laterally, mitigating their ability to access and leak data.
Ransomware attackers cannot see the different system components, target them and gain a foothold.see
Auditing and recording capabilities help detect breaches and prevent further damage.
Zero trust blackens the network, preventing attack methods like IP scanning.
Zero trust enhances potentially vulnerable VPNs by adding an extra layer of security.
Is the users’ data exposed?
Who has control of the access rules?
Where are our secrets (passwords, tokens, private keys) kept?
How is the risk of internal threats mitigated?
What is the scope of secure access? Does it include users, networks, apps, etc.?
What is the ZTNA provider’s infrastructure? Are the servers located in the cloud or in a data center? Who can access it?
What happens if the ZTNA provider is compromised? Is the organization still secure?
John Heywood, English playwright
Enable zero trust access for the most vulnerable and risky users with unknown security levels. These could include third parties, new employees added through M&A, remote employees using their own devices, etc.
Add zero trust connectivity for remote employees, especially those who are using a VPN and accessing critical applications.
Connect all employees and services to complete your digital transformation.
Step title
Add step text here