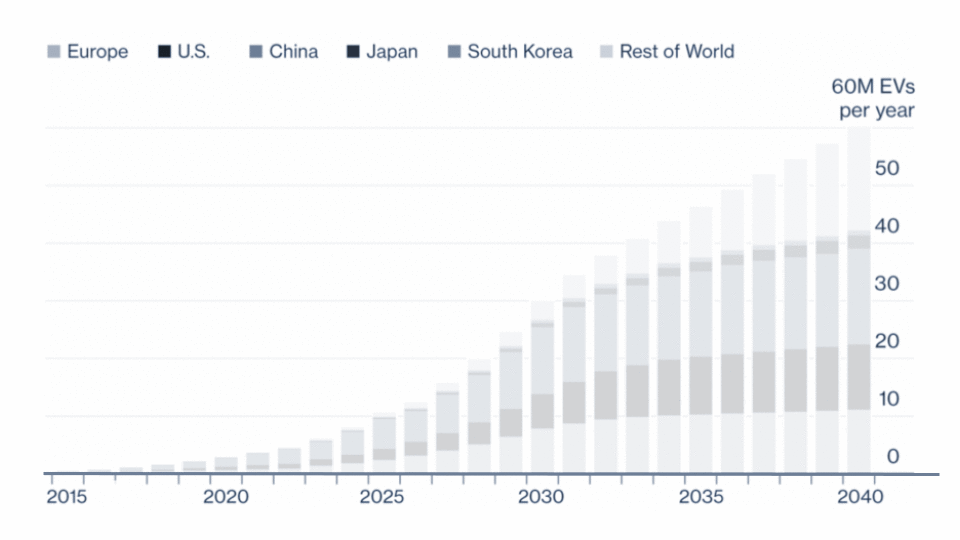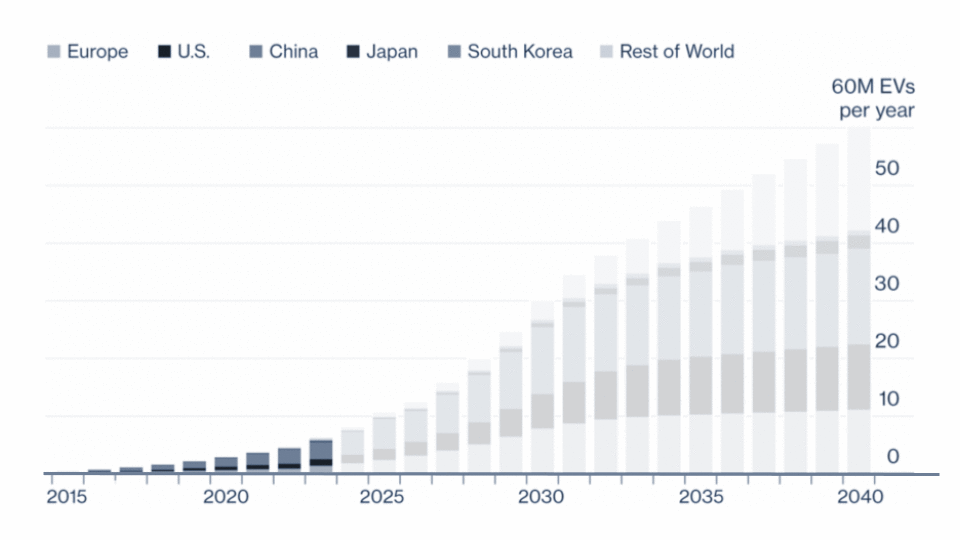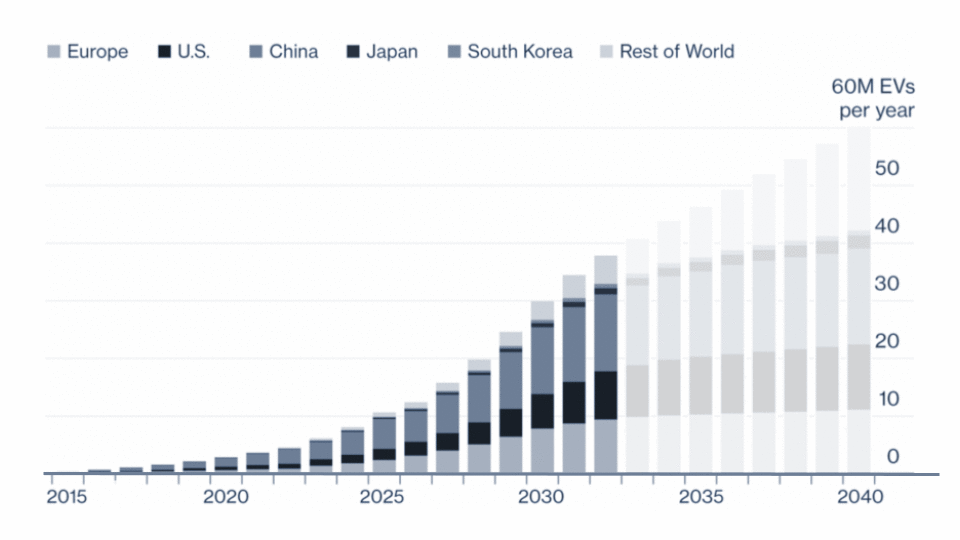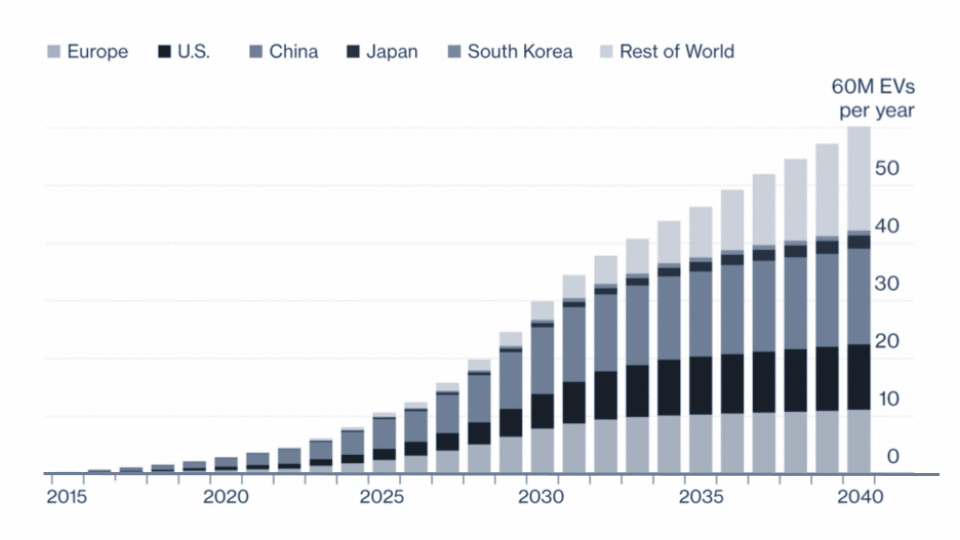
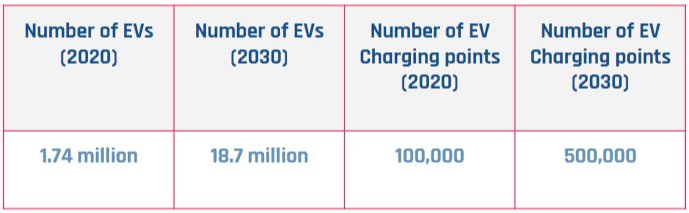
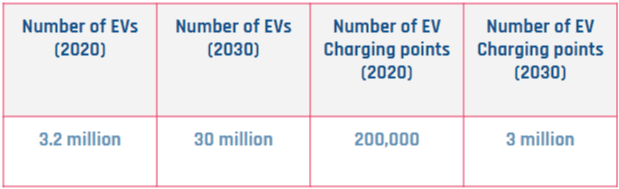
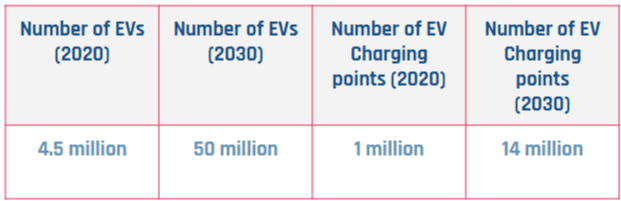
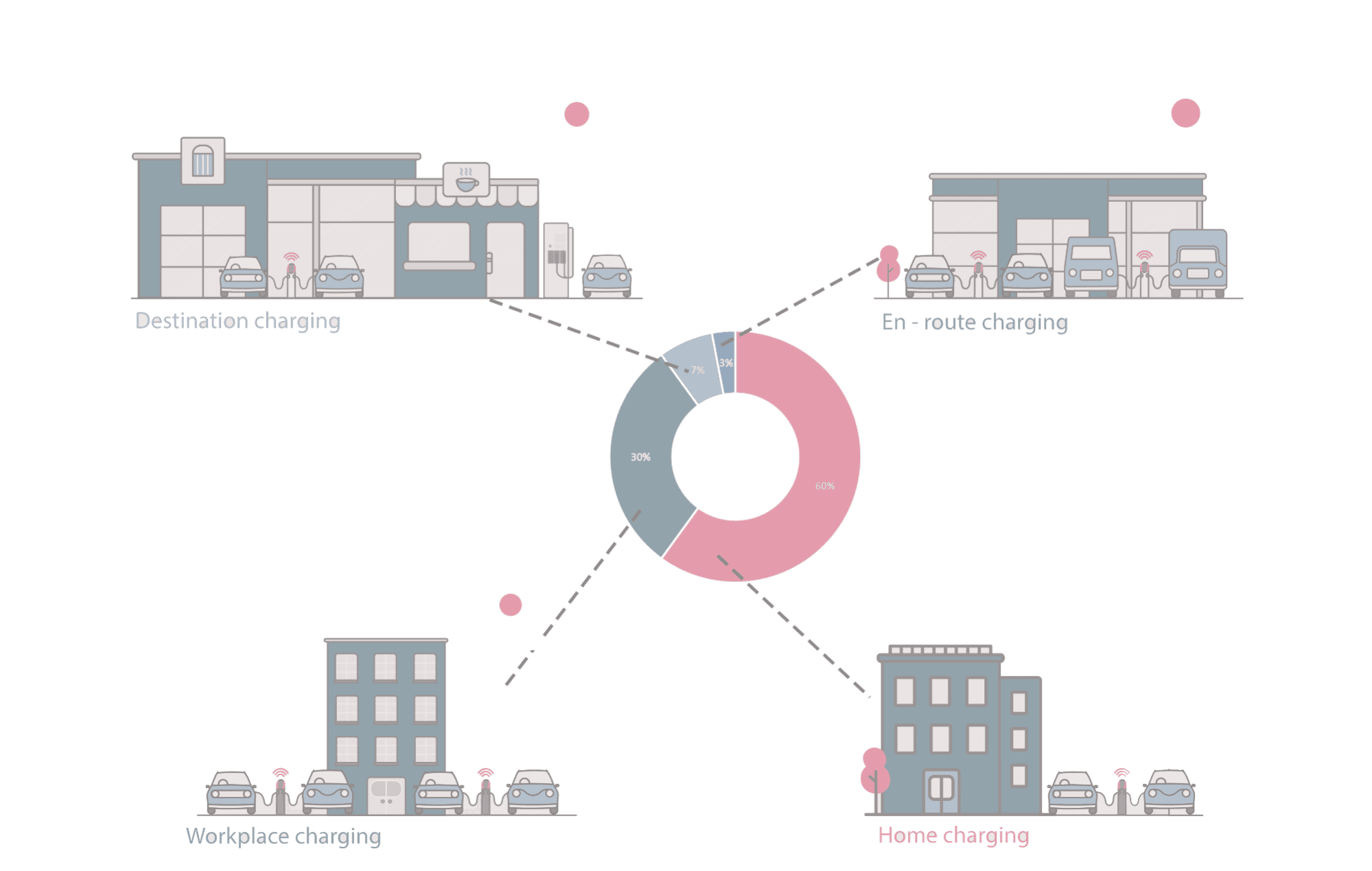
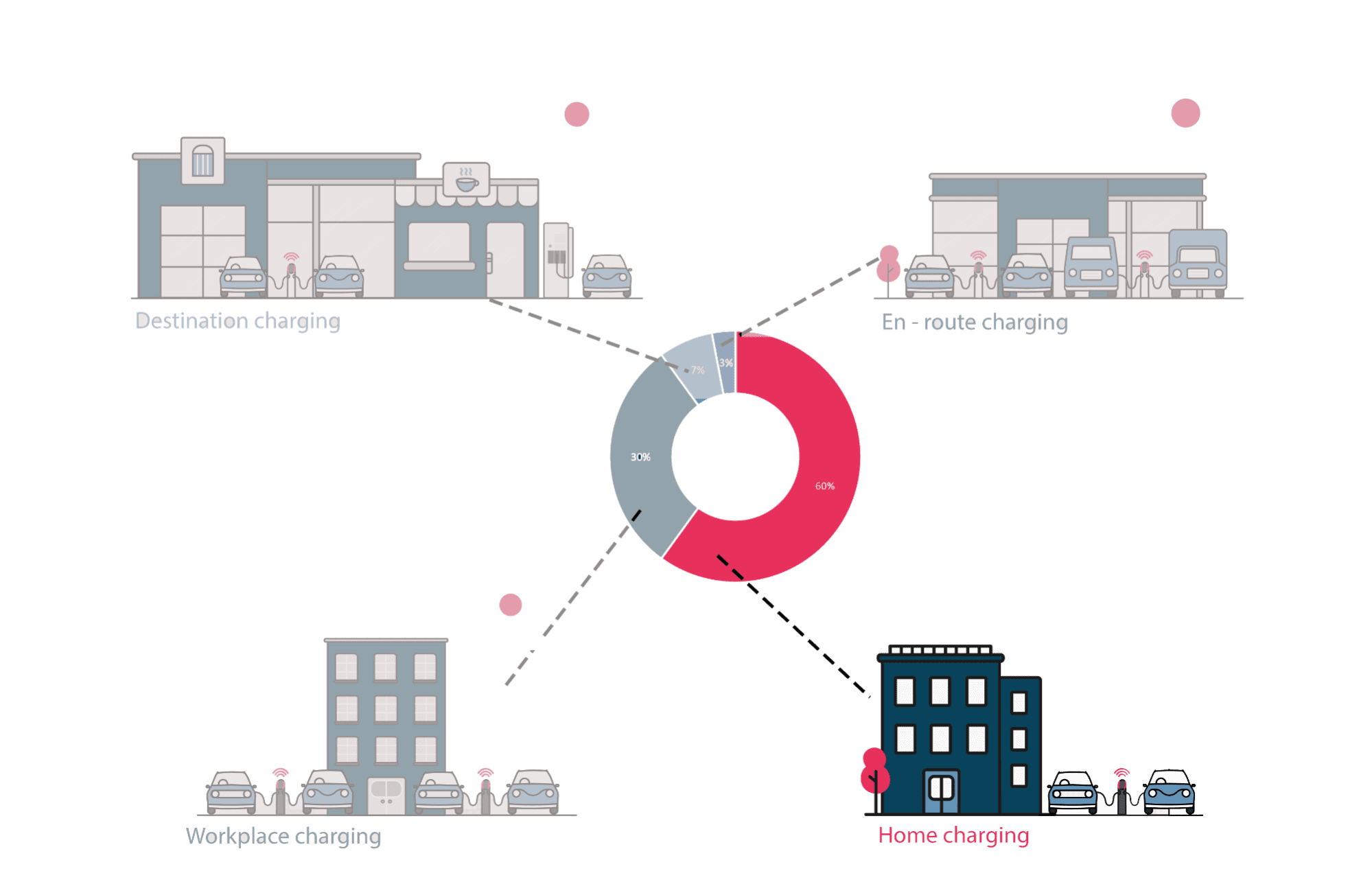
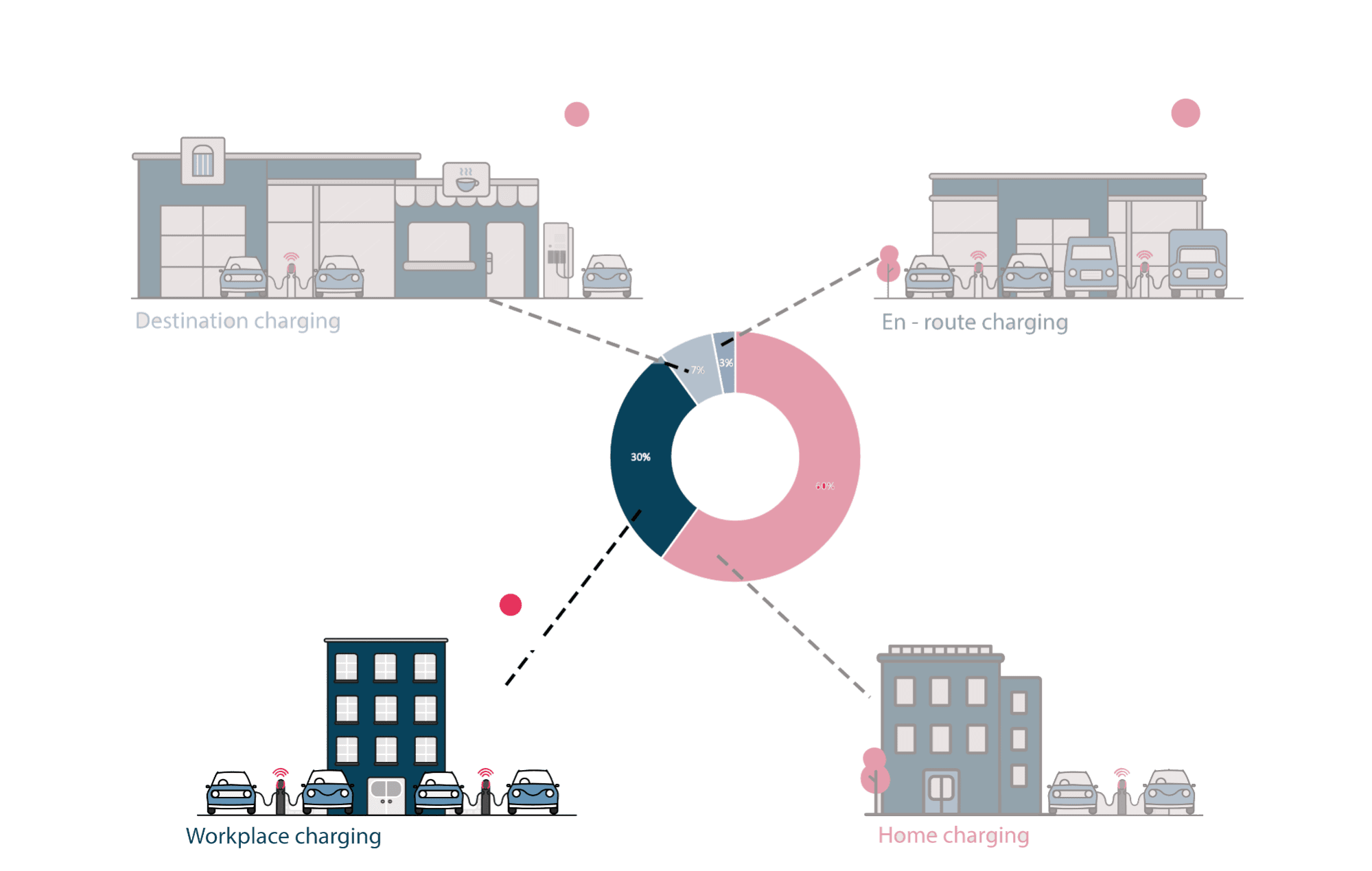
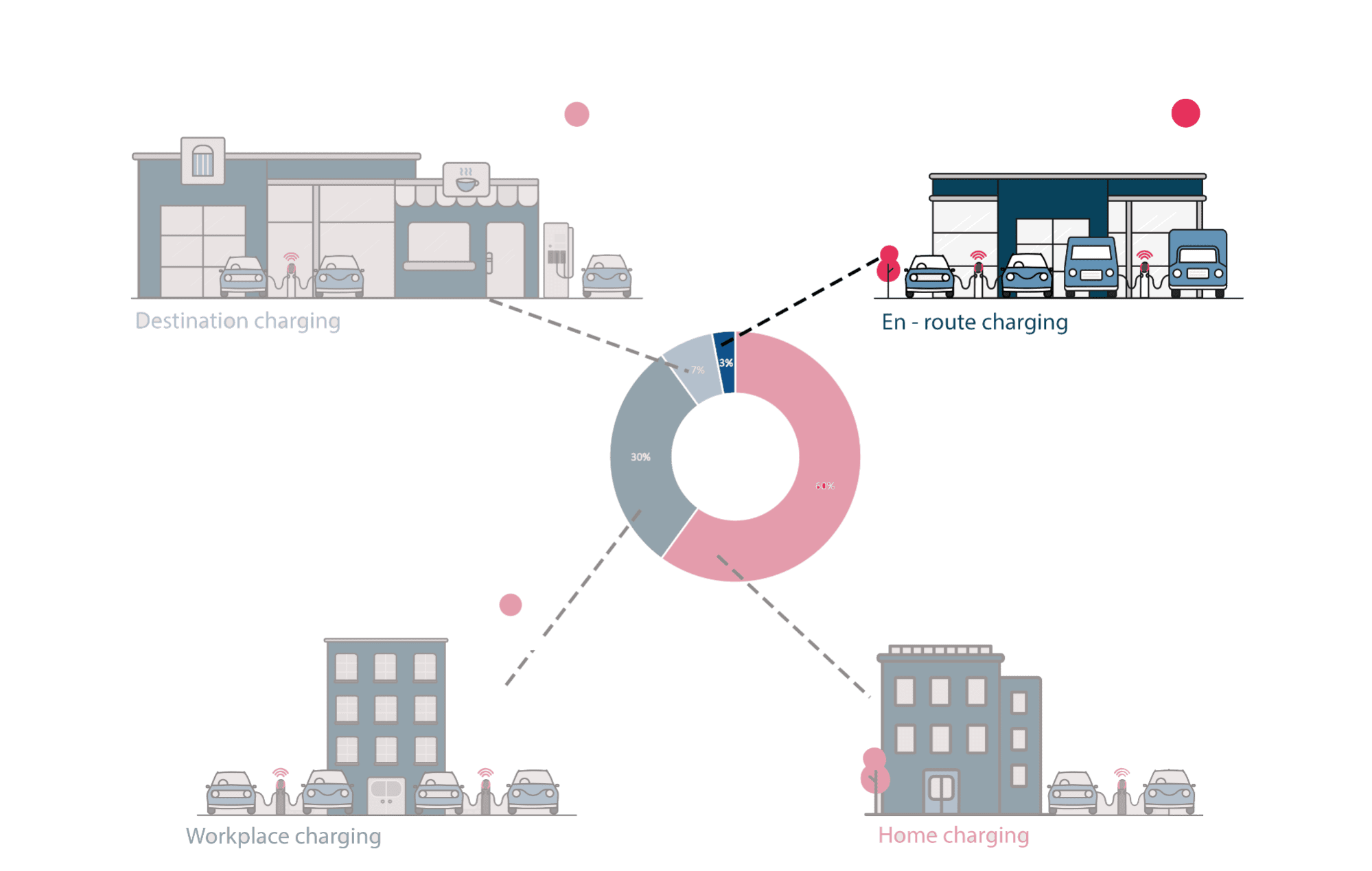
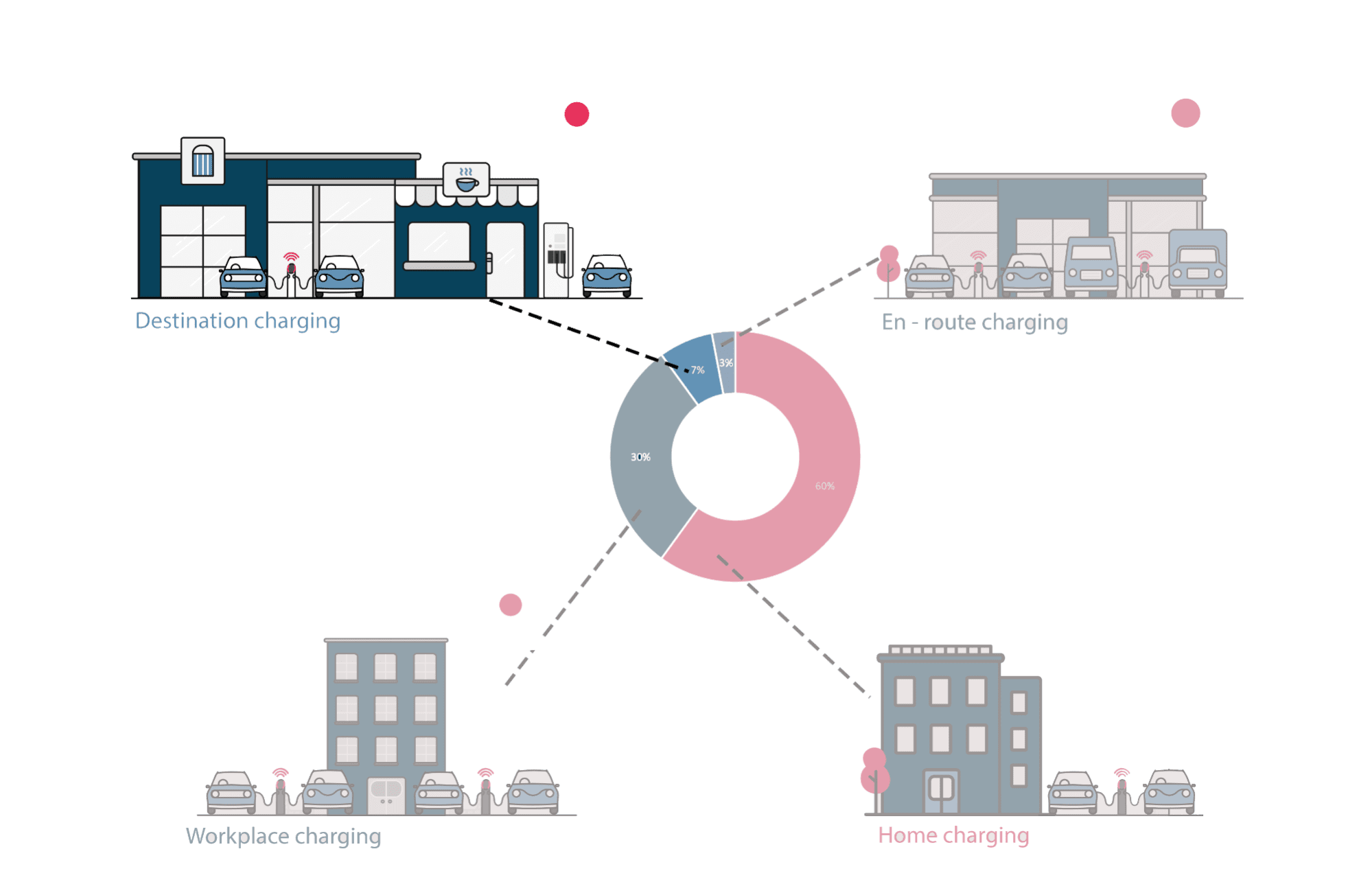
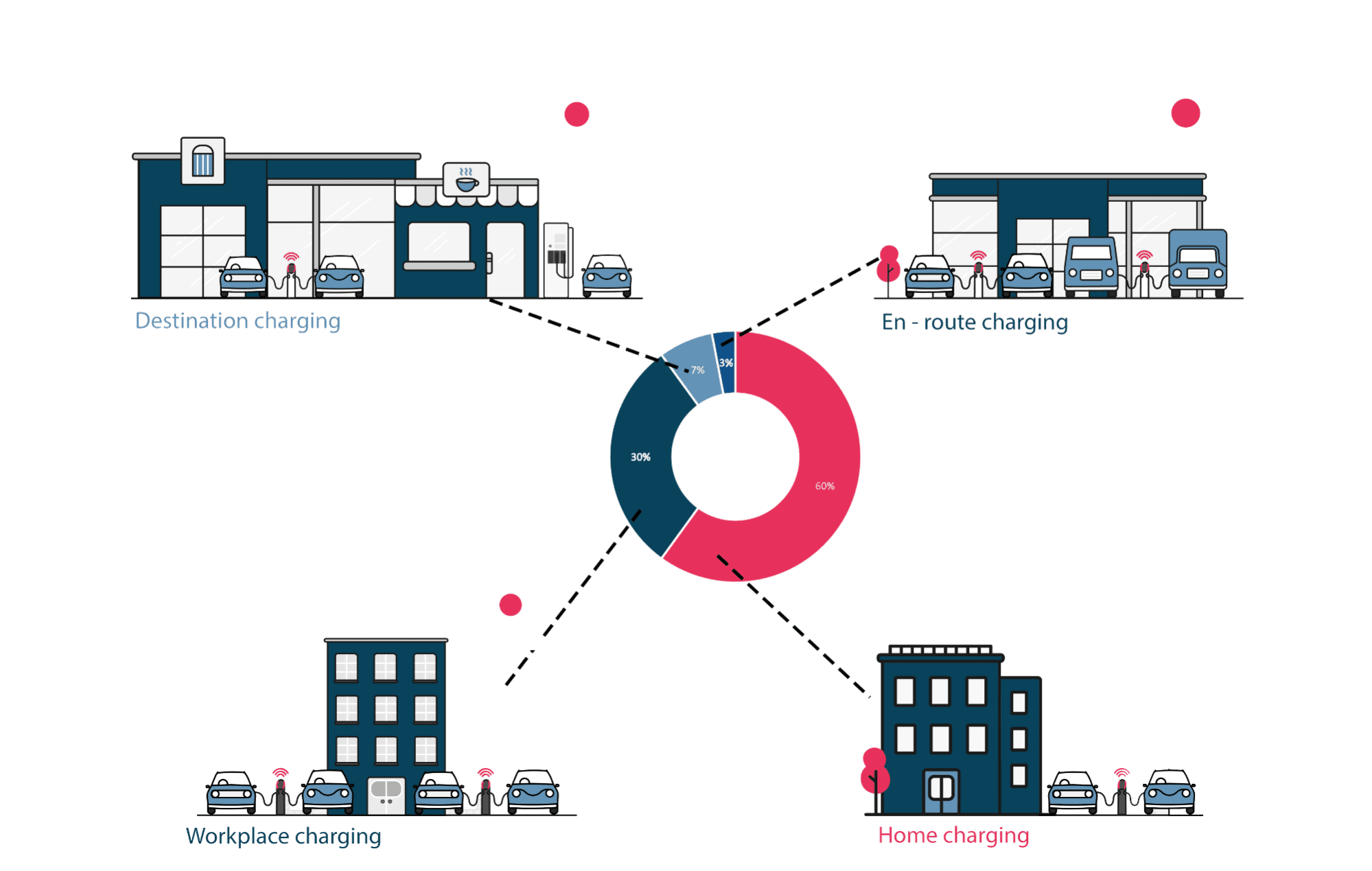
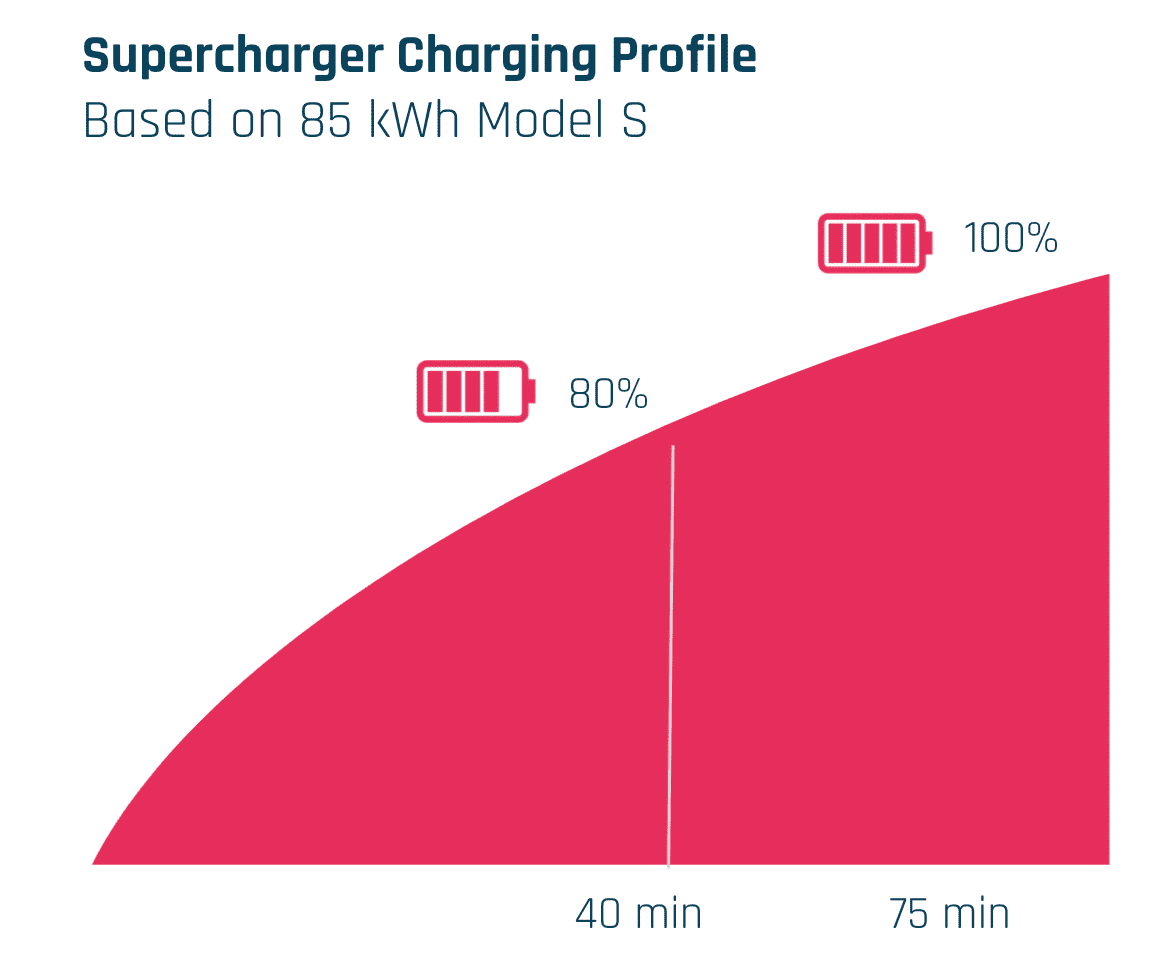
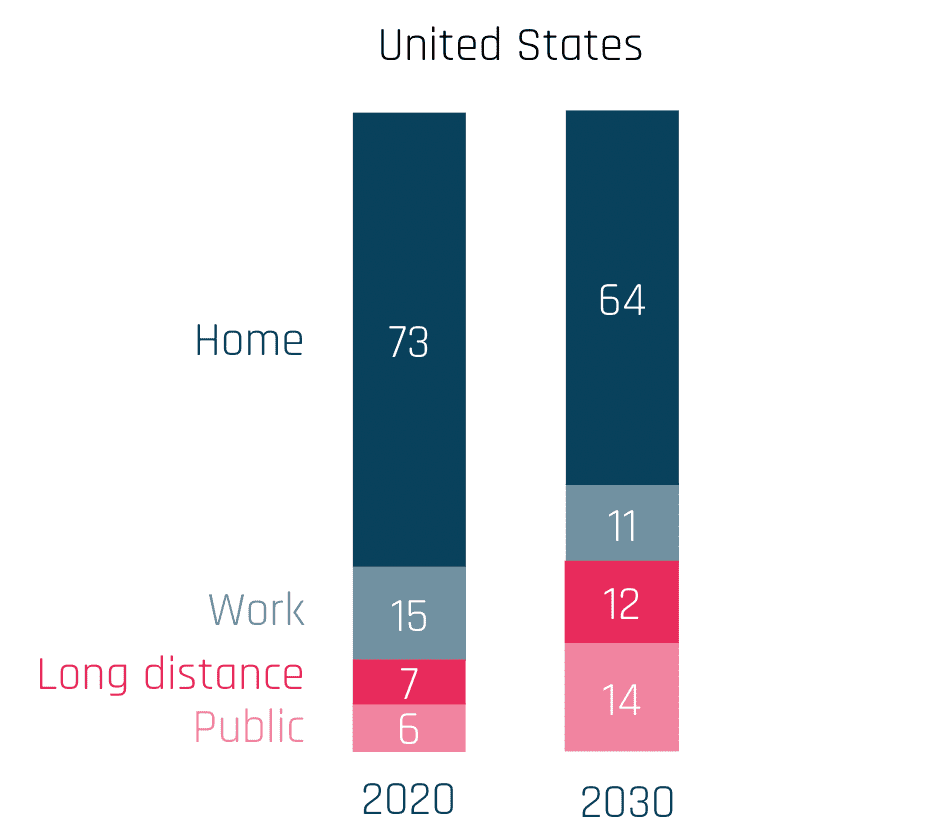
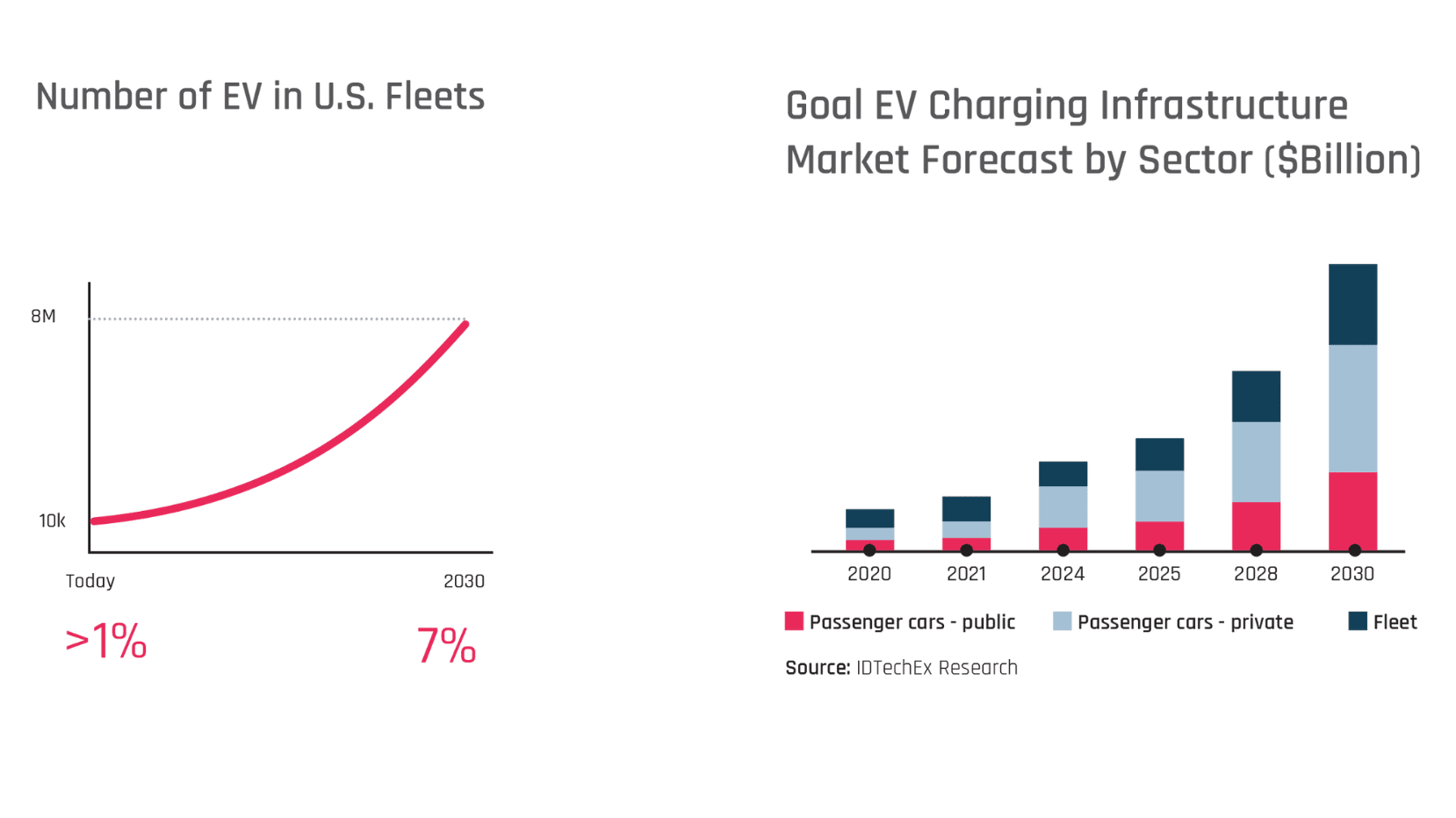
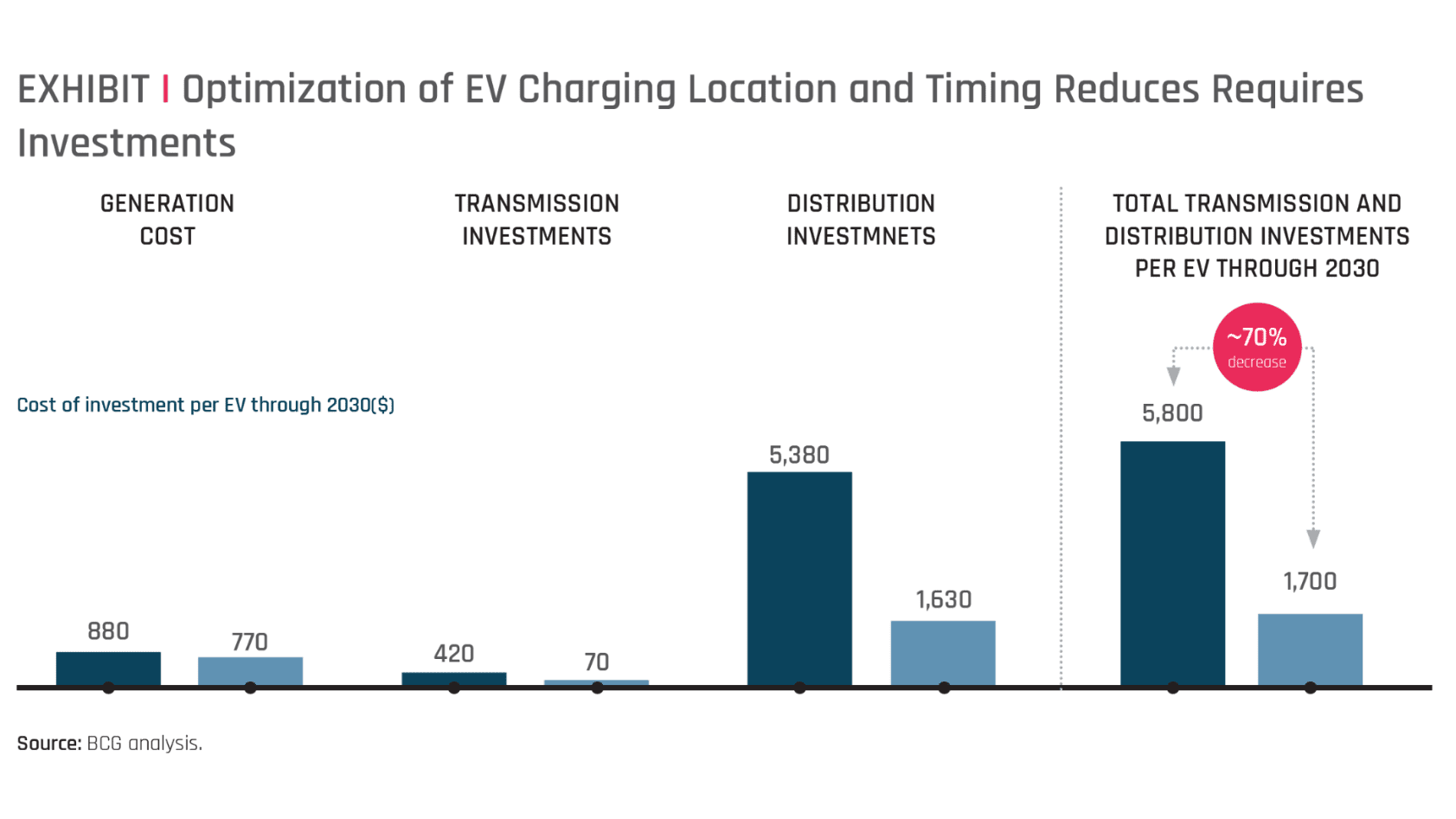
A charging point or station is the charging facility through which an EV is provided with electricity for recharging its battery. These can be found in 3 ways: Public charging infrastructure (when located in public places such as streets and highways), Semi-public charging infrastructure (when located in privately owned facilities such as parking lots, shopping malls, supermarkets or office buildings), and Private Charging infrastructure (when located in places not accessible to the general public, such as homes, apartment buildings or private parkings).
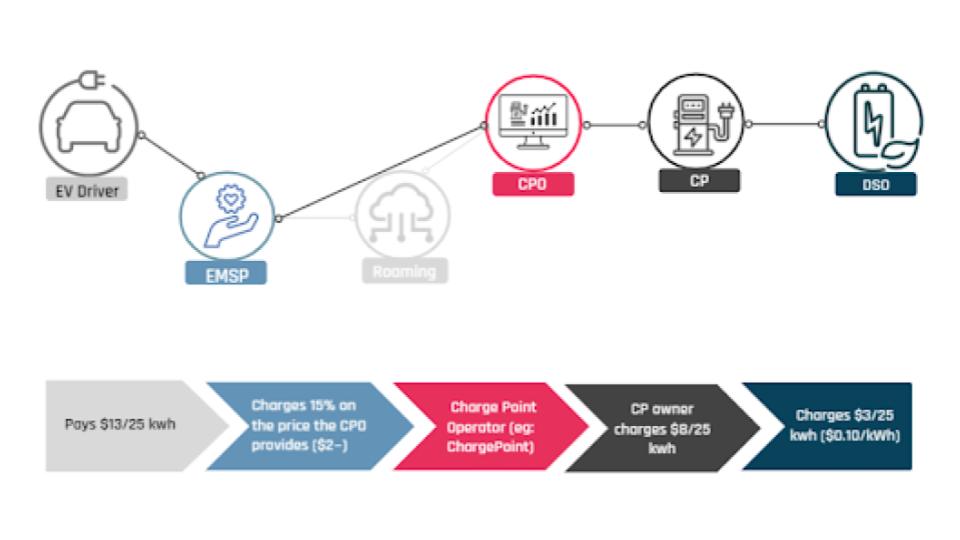
The CPO, or Charge Point Operator, is a company that manages a charging point network. CPOs handle diagnostics, device maintenance, and front-end support for their network. CPOs work alongside external facilitators known as Electric Mobility Service Providers, which provide external customers with access to their charging stations as a separate service. CPOs usually also offer a facilitation service in the form of an eMSP to the users of its network, which allows its own customers to access other CPO’s networks.
The eMSP, or electric mobility service provider, provides access to charging services for electric vehicle drivers and facilitates payment. eMSPs provide EV drivers with access to a variety of charging points around a geographical area. With the service, drivers can find available charging stations, start and stop charging and pay. eMSPs are the only entities that can access the EV users’ personal data.
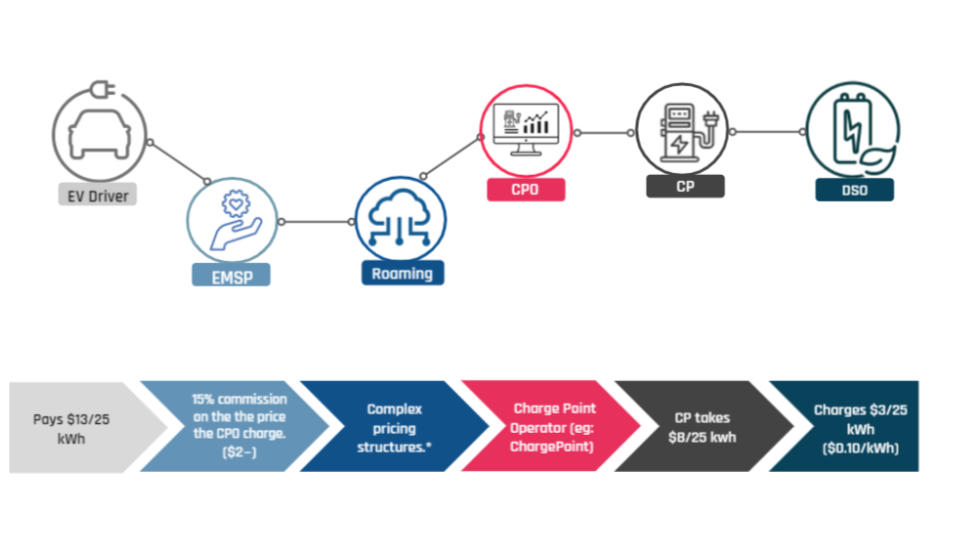
The eRoaming, or roaming networks allow electric vehicle drivers to connect to multiple charging stations, regardless of which service provider they are a customer. End customers of eMSPs have access to a wide network of CPOs, and different CPOs receive new business from the customers of several EMSPs. Through roaming agreements, they allow customers from one network to access another one without the need for any additional effort (like signing up for networks they don’t usually use). Thanks to eRoaming, a customer can simply register with one CPO network, carry one RFID card/membership tag, or have one app downloaded, and still have the ability to access all the other networks with which a roaming agreement is signed.
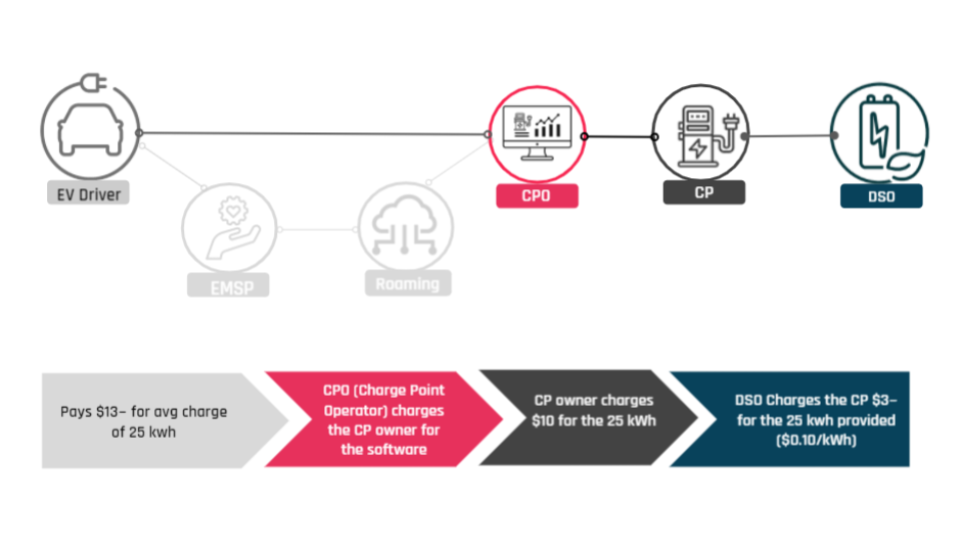
The DSOs (Distribution system operators) are responsible for operating (and sometimes owning) energy distribution networks. In this case, the DSO supplies the electricity for the Charge Point Owner.
The Charge Point Owners are different entities than Charge Point Operators. Charge Point Owners are usually not responsible for operating their chargers. They are responsible for providing the physical space where the chargers will be installed, preparing the electrical grid to support the chargers, buying and installing the chargers, and in some cases, providing maintenance for the chargers. The Charge Point Owners set the price per kWh or per minute to EV drivers for the electricity consumed, according to local regulations.